|
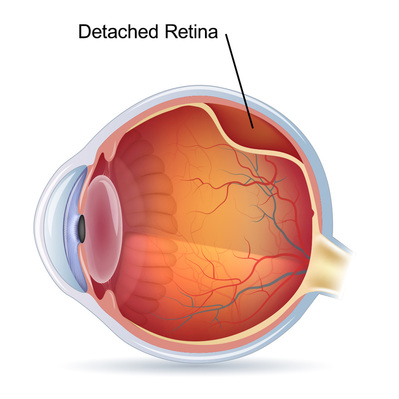
The retina is the light-sensitive tissue located at the back of the eye. Light passes through the eyes and focuses on the retina, which sends these signals to the brain.
Retinal detachment refers to instances in which damage to the retina result in the retina tearing and peeling away from its normal position. Serious physical trauma, problems with the vitreous gel within the eye, and certain illnesses may cause retinal detachment or tearing to occur. The DangerIf the retina detaches and is not treated in a timely fashion, a person may experience total vision loss. This can lead to permanent blindness.
|
Risk Factors
Some common risk factors associated with retinal detachment include the following:
- Advanced Age – When a patient is older than 40, risk of retinal detachment increases
- Previous Retinal Detachment – Any previous tears or detachment can increase the risk of a future retinal detachment
- Family History – When retinal tears and detachment run in the family, there is an increased risk of it happening to you
- Previous Severe Eye Injury – Suffering a serious eye injury in the past increases your risk of different eye problems, including retinal detachment
- Previous Eye Diseases or Disorders – As with eye injuries, conditions such as glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy can increase your risk of retinal detachment
- Previous Eye Surgery – Sometimes a previous eye surgery, even something as routine as a cataract removal, can make retinal detachment more likely
Warning Signs
It's important that you know what to look out for should a retinal injury occur. The most common signs of a retinal tear or detachment are:
- Flashes of Light – When the retina tears, you may notice brief yet bright flashes of light. This is the sign of the vitreous gel of the eye pulling at the damaged retina.
- Floaters – Floaters will accompany flashes. These little flecks, spots, and threads in the your vision are solid bits of the vitreous gel, and when many floaters appear in combination with a flash, it's very likely that the retina has been damaged.
- The Curtain Effect – The curtain effect means a dimming or graying of a person's overall field of vision. This is often a sign of the retina detaching and not functioning properly.